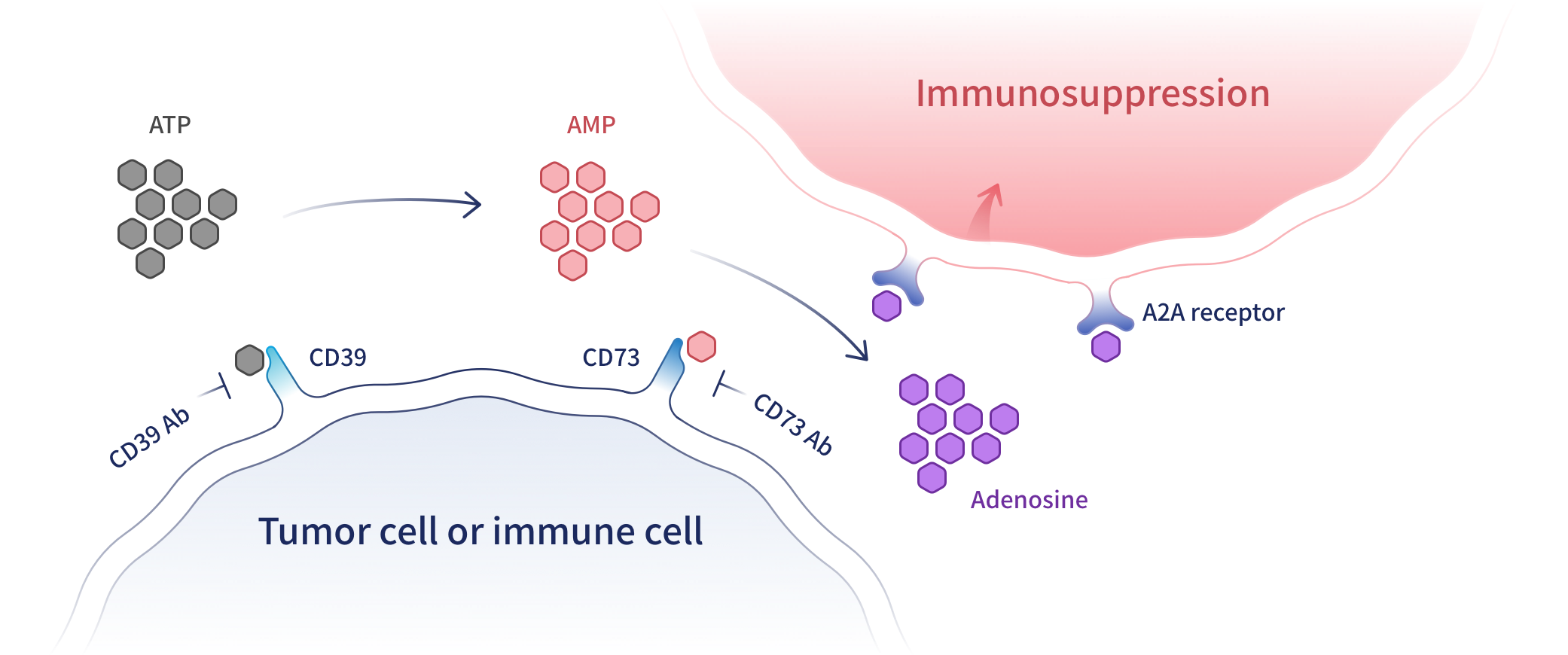
JAB-BX102 is a humanized monoclonal antibody, anti-CD73, developed by Jacobio. CD73 is a protein that plays a key role in the adenosine pathway, and its inhibition has broad therapeutic potential for tumors that are reliant on an active adenosine pathway. Combination treatment of JAB-BX102 with immune checkpoint drugs such as PD-(L)1 (anti-PD-1, or anti-PD-L1) antibodies, can result in synergistic anti-tumor efficacy. There are no anti-CD73 antibodies currently approved for cancer therapy.
CD73 also known as ecto-5'-nucleotidase, or Ecto5'NTase, is a membrane-bound/free protein that can hydrolyze AMP to adenosine. Adenosine inhibits the tumor immune response through interaction with the adenosine receptors, or P1 receptors, on the cell surface. CD73 is often highly expressed and indicative of a poor prognosis in various tumor tissues, including gastric cancer, renal cell carcinoma, prostate cancer, triple negative breast cancer, and non-small cell adenocarcinoma.
|
Asset |
Programs |
Region |
Phase |
Indication |
Registration information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
JAB-BX102 |
Monotherapy or Combo w/PD-1 mAb |
Global |
I |
Solid tumor |
ClinicalTrilas: NCT05174585 CDE Number: CTR20221114 |

Jacobio Pharma presented preclinical study data of JAB-X1800 at the 2023 AACR Annual Meeting